- The Great Lakes is the world’s largest surface freshwater system. Lake Superior, Lake Huron, Lake Michigan and Lake Erie all flow to the Niagara River.
- The total area drained by the Niagara River is approximately 684,000 km2.
- The Niagara River is 58 km in length, flowing north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario, to the St. Lawrence River and eventually out-letting to the Atlantic Ocean.
- The elevation difference between Lake Erie and Lake Ontario is 99 metres; Niagara Falls is 52 metres high.
- About 500 other waterfalls in the world are “taller” than Niagara Falls. The Angel Falls in Venezuela is tallest at 979 metres (3,212 ft.). However, some of the tallest falls in the world have very little water flowing over them. It’s the combination of height and volume that makes Niagara Falls so beautiful. More than 168,000 cubic metres (6 million cubic ft.) of water goes over the crest- line of the falls every minute during peak daytime tourist hours.
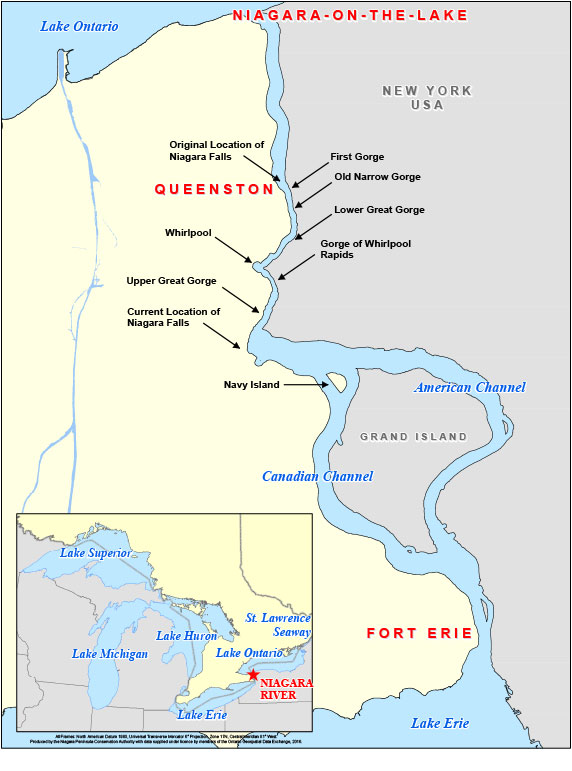
- Niagara Falls has receded 11.3 km (7 miles) in 12,500 years, and may be the fastest moving waterfalls in the world.
- At Grand Island, the Niagara River divides into the west channel, known as the Canadian Channel, and the east channel, known as the American Channel.
- The Niagara Gorge extends from the Falls for 11 kilometres (7 mi.) downstream to the foot of the escarpment at Queenston.
The waters of the Niagara River are used by a combined Canada/United States population of more than 1,000,000 people for a wide range of purposes, such as:
- Drinking water
- Recreation (boating, swimming, bird-watching)
- Fishing
- Industrial cooling water supply
- Receiver of municipal and industrial effluents
- Hydro-power generation (Sir Adam Beck Station in Ontario & New York State Power Authority)
